Chronic Conditions: The Aging Population
The aging population encounters a distinctive array of health challenges, further compounded by the widespread occurrence of multimorbidity (multiple chronic conditions). AWARENESS: Among the chronic conditions, heart disease is the leading cause of death for adults older than 65, followed by cancer, stroke, diabetes, chronic lower respiratory diseases, influenza and pneumonia, and, finally, Alzheimer's disease, as 63% of all deaths worldwide are from chronic conditions.[W] The interconnectedness of health conditions, such as obesity and its associated risk factors on diabetes, heart disease, and kidney disease, places limitations on self-care practices that, in turn, affect overall quality of life for older adults.
Chronic Conditions: Defined
Chronic health conditions, also known as chronic diseases or non-communicable diseases (NCDs), are long-term health conditions that persist over 3-12 and often progress slowly. AWARENESS: Unlike acute conditions, which have a sudden onset on a portion of the body and a shorter duration, chronic conditions are manageable through the uses of treatment but typically do not progress to a terminal stage. These conditions often have complex causes, including genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Examples of chronic health conditions include:
-
Cardiovascular Diseases: Conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels, such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, and hypertension.
-
Diabetes: A group of metabolic disorders characterized by high blood sugar levels, either due to inadequate insulin production or the body's ineffective use of insulin.
-
Chronic Respiratory Diseases: Conditions affecting the respiratory system, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and interstitial lung diseases.
-
Cancer: Abnormal cell growth that can invade and destroy surrounding tissues. Cancer encompasses various types affecting different organs and systems.
-
Chronic Kidney Disease: The gradual loss of kidney function over time, leading to impaired filtration of waste and excess fluids from the blood.
-
Arthritis: Inflammation of the joints, resulting in pain, swelling, and stiffness. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are common forms of arthritis.
-
Neurological Disorders: Conditions affecting the nervous system, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and multiple sclerosis.
-
Obesity: A condition characterized by excessive body weight, often leading to other chronic health issues such as cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.
-
Mental Health Disorders: Conditions affecting mental well-being, including depression, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia.
-
Digestive System Disorders: Chronic conditions affecting the gastrointestinal tract, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and chronic liver disease.
Chronic Conditions: Prevention Strategies
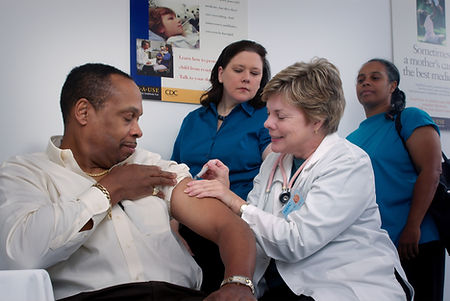
Preventive strategies play a crucial role in maintaining health and well-being, particularly in the context of chronic conditions. The significant influence of early intervention may results in less severe outcomes. These strategies aim to proactively reduce the risk of developing health issues and mitigate the impact of existing conditions.
AWARNEESS: Implementing self-care and accountability measures can aid in the mitigation and onset of many chronic conditions. Emphasizing proactive habits, self-care plays a pivotal role in fostering healthy lifestyle choices and preventing health deterioration.
-
Lifestyle Choices: Encourage healthy habits like regular exercise, a balanced diet, weight management, and avoiding harmful behaviors.
-
Regular Check-ups: Emphasize routine health check-ups and screenings for early detection of potential health issues.
-
Immunizations: Advocate for vaccinations to prevent infectious diseases and contribute to community immunity.
-
Health Education: Provide information and raise awareness about healthy behaviors, risk factors, and the importance of preventive care.
-
Chronic Disease Management: Implement programs to educate and support individuals in managing chronic conditions effectively.
-
Mental Health Support: Promote mental health awareness, stress management techniques, and access to mental health services.
-
Workplace Wellness: Introduce workplace wellness programs promoting fitness, healthy eating, and stress reduction.
-
Community Interventions: Create community environments that support health through access to recreational spaces and healthy options.
-
Genetic Counseling: Provide genetic counseling and testing for individuals with a family history of certain conditions.
-
Policy Initiatives: Implement policies regulating tobacco and alcohol, promoting healthy school environments, and encouraging physical activity.
-
Technology in Healthcare: Utilize telehealth and remote monitoring for remote access to healthcare services and early intervention.

Obesity Crisis
COMING SOON!
Alzheimer's Disease
COMING SOON!







